

The basis of social learning theory is simple: People learn by watching other people. We can learn from anyone—teachers, parents, siblings, peers, co-workers, YouTube influencers, athletes, and even celebrities. We observe their behavior and we mimic that behavior. In short, we do what they do. This theory is also known as social cognitive theory.

Social learning theory, developed by psychologist Albert Bandura, uses theories of classical and operant conditioning. But in this theory, the environment plays a large part in learning. We model the behavior of the people around us, especially if we find these models similar to ourselves or if we want to emulate them.
What are the elements of social learning theory? Created with Sketch.There are different parts to this theory. First, we learn by observing others. Second, our mental state is important in the learning process. Third, learning doesn’t mean there will be a change in behavior.
What is a good example of social learning theory? Created with Sketch.The YouTube influencer is a good case in point. If you like a particular influencer you may well want to model your behavior after hers. If she enjoys a certain brand of shampoo, then you may well imitate her by purchasing that brand.
What are the processes of observational learning? Created with Sketch.Observational learning requires these four processes: attention, retention, reproduction, motivation. You have to pay attention to imitate behavior, retain or remember the behavior, reproduce the behavior, be motivated to reproduce it.
article continues after advertisement What the Bobo Doll Taught Us
Bandura developed what famously became known as the Bobo Doll experiments. In these studies, children watched adults model either violent or passive behavior towards a toy, the Bobo Doll. What the children saw influenced how they themselves subsequently interacted with the doll. Specifically, children who observed violent behavior imitated this behavior and were verbally and physically aggressive toward the doll. Children who witnessed nonviolent behavior behaved less aggressively toward the doll. In recent years, some psychologists have called Bandura’s original findings into question, labeling his experiments as biased, poorly designed, or even unethical.
What did we learn from the Bobo Doll experiment? Created with Sketch.Albert Bandura concluded that children learn aggression, violence, and other social behaviors through observation learning, or watching the behaviors of others. On the opposite end, kindness and compassion can be imitated as well.
Is social learning theory still viable and applied? Created with Sketch.Despite the criticisms, Bandura’s larger theory is still applied by psychologists seeking to understand the roots of behavior and mood, the importance of role models, and to glean insight into consumer purchasing decisions.
Different Learning Theories
Learning theory tells us how we take in and process information and knowledge. A person’s environment influences his learning. In the case of Pavlov’s dog, for example, the physiologist Ivan Pavlov found that the sound of a metronome produced saliva in a dog’s mouth. The dog was conditioned to hear the sound and associate that sound with food, hence the salivation. This is called classical conditioning.
In operant conditioning, coined by B.F. Skinner, we learn through reinforcement or punishment. We avoid touching a pot of boiling water, for example, because we will burn our fingertips. Skinner developed the operant conditioning chamber, later known as the Skinner Box, to study animal behavior. The chamber or box has a key or bar that can be pressed so that the animal obtains a reward like food or water. Manipulating the key meant food, that is the premise of reinforcement in learning.
What is an example of a classical conditioning? Created with Sketch.Food poisoning is a good example of such conditioning. If your first experience of eating a burrito ended in nausea and other contaminated food symptoms, you will likely gag at the smell of future similar dishes.
What is an example of operant conditioning? Created with Sketch.The sales incentive is positive reinforcement in operant conditioning. The quarterly bonus, for instance, is offered to the sales agent who reaches his target goal. And he will likely strive to reach his future goals with such a stimulus.
Essential Reads

Research is proving that the extraordinary cognitive abilities of tiny creatures are not science fiction.

Conventional language influences the initial imitation of a model's use of an inefficient tool. But a pressured task decreases children's willingness to copy inefficient actions.
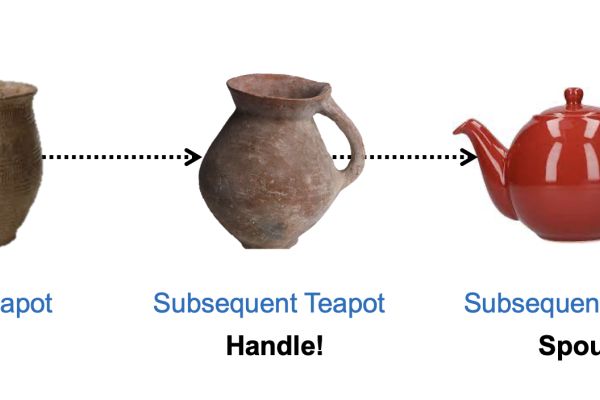
By entering your own actions and ideas, you’ll see how they pave the way for other cultural developments, and see where they fit into the interwoven tapestry of human achievements.

Gen X parents worry about crime happening to their children but often fear the wrong crimes, emphasizing stranger danger.
Gen X parents worry about crime happening to their children but often fear the wrong crimes, emphasizing stranger danger.

Babies born early are typically placed in incubators, but many would do better on their parents’ chests.
Babies born early are typically placed in incubators, but many would do better on their parents’ chests.

Summer is here, and children and teens are out of their normal routine. Let's continue to encourage social-emotional learning during this time.
Summer is here, and children and teens are out of their normal routine. Let's continue to encourage social-emotional learning during this time.

Abigail Shrier’s new book, "Bad Therapy," criticizes therapeutic education but without helping us to see why educators and parents might find it convincing, even inspiring.
Abigail Shrier’s new book, "Bad Therapy," criticizes therapeutic education but without helping us to see why educators and parents might find it convincing, even inspiring.

Believing in others transcends liking them or helping them out of obligation. Here are some suggestions for nurturing these transformative relationships.
Believing in others transcends liking them or helping them out of obligation. Here are some suggestions for nurturing these transformative relationships.

Have you ever wondered why it is so hard to stop drinking? Dive into the reasons behind each sip.
Have you ever wondered why it is so hard to stop drinking? Dive into the reasons behind each sip.

Studies show that experiencing marital conflict as a child makes people more vulnerable to conflict in their adult romantic relationships. Here's how to stop the cycle.
Studies show that experiencing marital conflict as a child makes people more vulnerable to conflict in their adult romantic relationships. Here's how to stop the cycle.
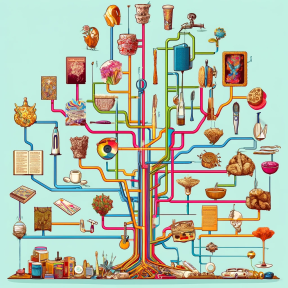
Social learning and individual learning play similar roles; they transmit existing knowledge and catalyze the creative generation of new knowledge and, thereby, cultural change.
Social learning and individual learning play similar roles; they transmit existing knowledge and catalyze the creative generation of new knowledge and, thereby, cultural change.

To build the cultural equivalent of evolutionary trees, it is necessary to distinguish the individual learning of existing information from the creation of new information.
To build the cultural equivalent of evolutionary trees, it is necessary to distinguish the individual learning of existing information from the creation of new information.

What is courage? Is courage defined differently for men and women? Is courage socially conditioned, innate, or some mixture of nature and nurture? Can courage be learned?
What is courage? Is courage defined differently for men and women? Is courage socially conditioned, innate, or some mixture of nature and nurture? Can courage be learned?